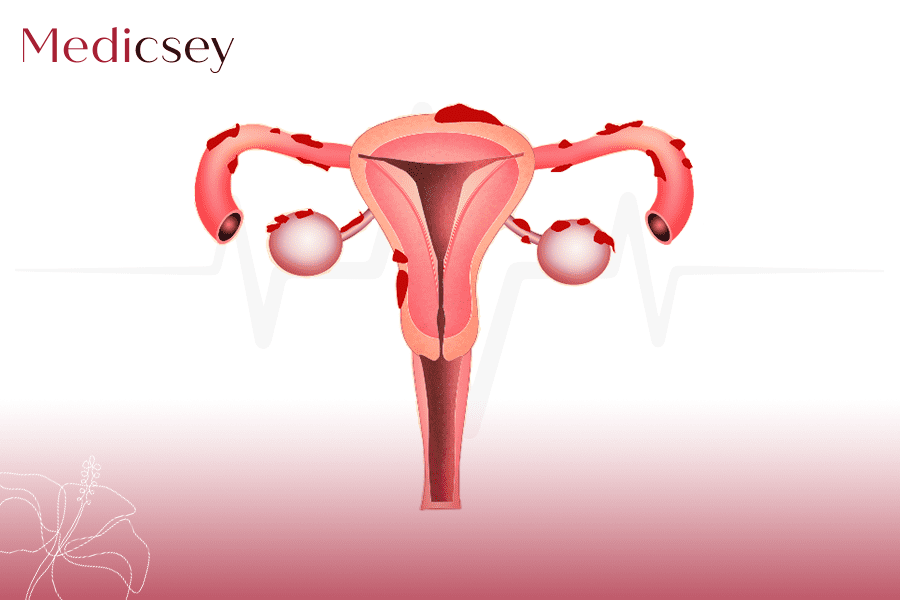
Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the womb starts to grow in other places, such as the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
Endometriosis can affect women of any age.
It's a long-term condition that can have a significant impact on your life, but there are treatments that can help.
Symptoms of endometriosis
The symptoms of endometriosis can vary. Some women are badly affected, while others might not have any noticeable symptoms.
The main symptoms of endometriosis are:
- pain in your lower tummy or back (pelvic pain)– usually worse during your period
- period painthat stops you doing your normal activities
- pain during or after sex
- pain when peeing or pooing during your period
- feeling sick, constipation, diarrhoea, or blood in your pee during your period
- difficulty getting pregnant
You may also have heavy periods. You might use lots of pads or tampons, or you may bleed through your clothes.
For some women, endometriosis can have a big impact on their life and may sometimes lead to feelings of depression.
Treatments for endometriosis
There's currently no cure for endometriosis, but there are treatments that can help ease the symptoms.
Treatments include:
- painkillers – such as ibuprofenand paracetamol
- hormone medicines and contraceptives – including the combined pill, the contraceptive patch, an intrauterine system (IUS), and medicines called gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogues
- surgery to cut away patches of endometriosis tissue
- an operation to remove part or all of the organs affected by endometriosis – such as surgery to remove the womb (hysterectomy)
Your doctor will discuss the options with you. Sometimes they may suggest not starting treatment immediately to see if your symptoms improve on their own.
Further problems caused by endometriosis
One of the main complications of endometriosis is difficulty getting pregnant or not being able to get pregnant at all (infertility).
Surgery to remove endometriosis tissue can help improve your chances of getting pregnant, although there's no guarantee that you'll be able to get pregnant after treatment.
Surgery for endometriosis can also sometimes cause further problems, such as infections, bleeding or damage to affected organs.
If surgery is recommended for you, talk to your surgeon about the possible risks.
Living with endometriosis
Endometriosis can be a difficult condition to deal with, both physically and emotionally.
As well as support from your doctor, you may find it helpful to contact a support group.
Causes of endometriosis
The cause of endometriosis is not known.
Several theories have been suggested, including:
- genetics – the condition tends to run in families, and affects people of certain ethnic groups more than others
- retrograde menstruation – when some of the womb lining flows up through the fallopian tubes and embeds itself on the organs of the pelvis, rather than leaving the body as a period
- a problem with the immune system, the body's natural defence against illness and infection
- endometrium cells spreading through the body in the bloodstream or lymphatic system, a series of tubes and glands that form part of the immune system
But none of these theories fully explain why endometriosis happens.
It's likely the condition is caused by a combination of different factors.