Polycystic ovary syndrome is a hormonal disorder that is more common among women in their reproductive years and symptoms often begin to appear in adolescence. Treatment may help clear symptoms and prevent long-term complications.
Table of Contents
Polycystic ovary syndrome
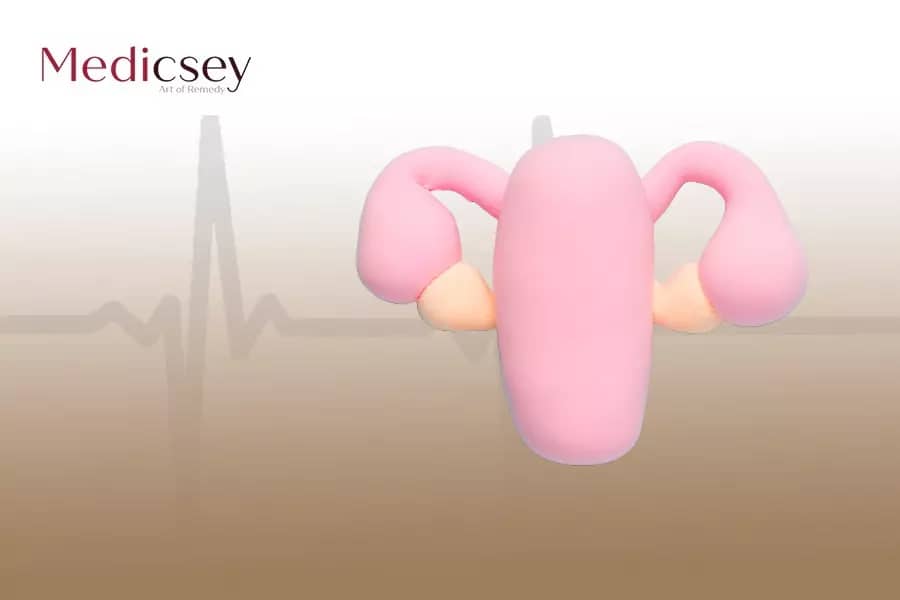
Polycystic ovary syndrome is also known by another name called polycystic ovaries. Ovarian syndrome can cause hormonal imbalances and is often associated with a rise in androgen levels and the presence of small, fluid-filled cysts on the ovaries. Polycystic ovary syndrome is the primary cause of infertility
Symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome
Symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome are mild in their initial stages, and some of these symptoms may appear, or symptoms may be severe. We mention these symptoms:
- Acne.
- Overweight.
- Hirsutism in the face and body, hair on the face often becomes thick and dark in color, and hair growth on the back, abdomen and chest increases.
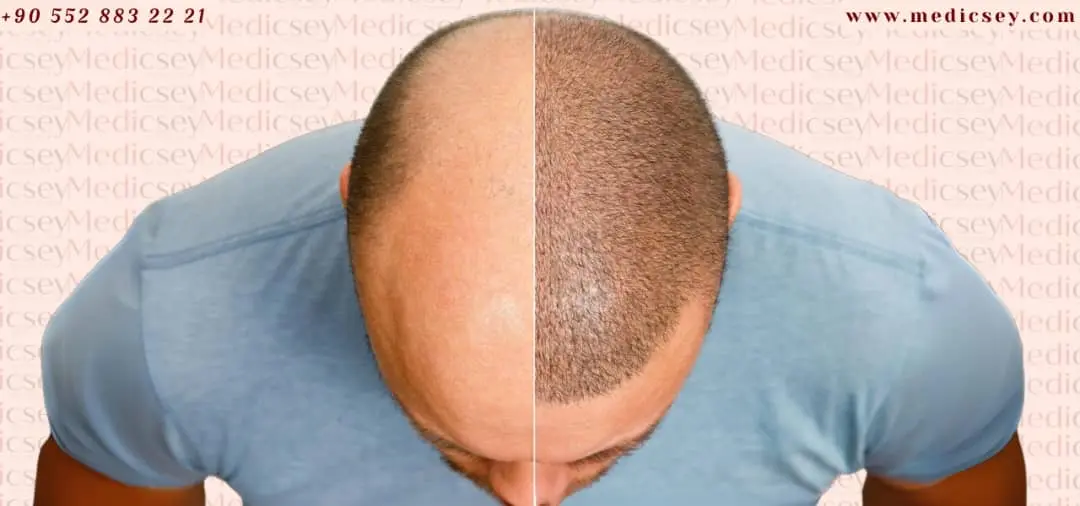
- Decreased hair density on the head.
- Irregular menstrual cycle.
- Infertility or fertility problems.
- Depression.
In most women with polycystic ovary syndrome, many small cysts grow on the ovaries. Hence the name of this phenomenon polycystic ovary syndrome, these cysts are not harmful, but they cause confusion and disruption of the hormonal balance in the body.
Causes of polycystic ovary syndrome
The causes of PCOS are not precisely known. However, a high level of androgen leads to an imbalance in reproductive hormones and ovarian dysfunction affect the formation and release of eggs normally.
A high level of androgen is associated with many reasons including the following:
- Genetic causes: Women whose mothers have suffered from PCOS or type II diabetes are considered. More likely to develop polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Insulin resistance: About 70% of women with polycystic ovary syndrome have insulin resistance. Genetics combined with unhealthy diet, lifestyle and obesity are causes of insulin resistance.
- Inflammation: Women with PCOS often suffer from inflammation and this can play a role in the high level of androgen in the body. Being overweight increases the risk of increased chances of inflammation.
Diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome
To diagnose polycystic ovary syndrome, your doctor must:
- Ask the patient about the medical history and accompanying symptoms.
- Perform a physical examination to investigate the symptoms of the syndrome, such as: the presence of hirsutism in the body.
Measure weight and height, so your doctor can make sure your BMI is within normal limits.
- Conducting several laboratory tests to check the level of sugar in the blood, insulin, and the levels of other hormones, to rule out the presence of a defect in the thyroid gland. Which can cause symmetrical symptoms.
- Pelvic tomography to detect cyst in the ovaries.
Treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome
There is no cure for PCOS definitively, but therapeutic procedures aim to control and prevent symptoms and complications. The treatment of PCOS is divided into two main parts:
- Follow a healthy lifestyle and a balanced diet.
- Drug therapy.
- Surgery may sometimes be used to improve fertility, where small holes are made in the ovary to restore normal ovulation. Using a thin needle or laser.
Non-pharmacological PCOS treatment
Treatment for polycystic ovary syndrome involves a healthy lifestyle, including:
Following a low-carb diet and weight loss, as losing 5-10% of weight can help improve associated symptoms. Especially if you are overweight patient.
- Regular exercise which helps to reduce weight, and increase the body's sensitivity to insulin.
Polycystic ovary syndrome drugs
Some medications are prescribed to control symptoms, including the following:
- Birth control pills
Birth control pills containing the hormones estrogen and synthetic progesterone help lower the level of androgen. Thus regulating the menstrual cycle and treating endogenic symptoms, such as hair growth and acne, also reduces the risk of endometrial cancer.
Another treatment that may be followed to regulate the menstrual cycle is to take progesterone pills for 10 to 14 days each month. But this method does not affect androgen levels.
- Metformin
This drug is used to treat type II diabetes. It is used in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome to reduce associated insulin resistance.
- Clomiphene
This medication is an ovulation and fertility stimulator and helps treat pregnancy problems caused by polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Spironolactone
Spironolactone helps reduce excess hair due to its role in lowering androgen levels.
Some treatments are prescribed to reduce unwanted hair growth, such as Efflornithin cream, a medicine that slows hair growth.
Prevention of polycystic ovary syndrome
There are some tips to prevent polycystic ovary syndrome, the most important of which are:
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Exercise regularly.
- Maintain a normal blood sugar level and take antidiabetic drugs in the event of diabetes.
The cost of polycystic ovary syndrome treatment in Turkey
There are many factors that affect the cost of PCOS treatment, including:
- Type of treatment.
- The goal of treatment is weight loss, symptom relief or successful pregnancy.
- Duration of treatment.
- The severity of symptoms.
- Patient's age.
- Other comorbidities.
Turkey has a very high level of extensive experience of its doctors, the infrastructure of its hospitals and the medical services it provides. In addition, their prices are very low in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome.
In conclusion, we have learned about polycystic ovary syndrome in Turkey and how to treat it. For more information, you can contact Medicsey Center to provide free and immediate consultation by the most skilled gynecologists in Turkey
read more: IVF Tube Baby
The cost of infertility treatment in Turkey